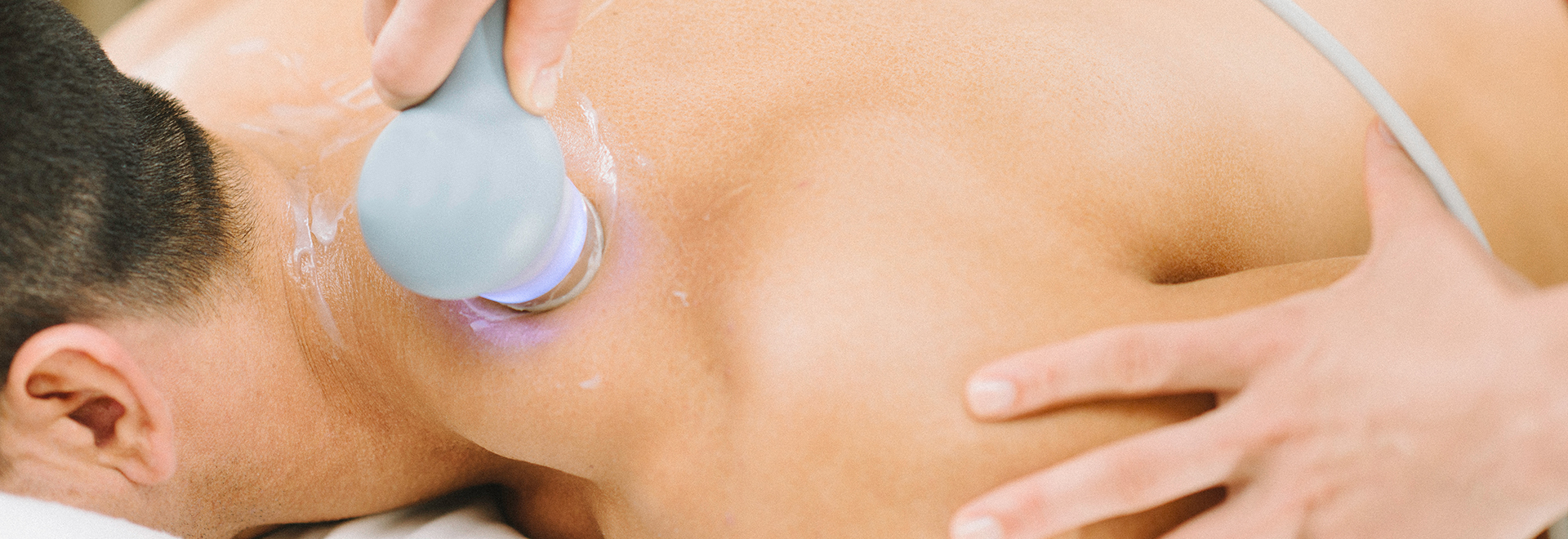
It is not uncommon for city-dwellers living with various muscle strains and aches due to incorrect posture sitting at the office or doing sports. As such, many look for physiotherapists to ease their discomfort and pain. Apart from manual therapy, ultrasound therapy, extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) and interferential current therapy (IFC) are also employed to facilitate recovery. However, could you tell the differences between these therapies? And do you know if you are suitable to receive these treatments?
Differences Between Ultrasound Therapy, Interferential Current Therapy and Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy
These non-invasive therapies aim to reduce inflammation and relieve sore muscles. The table below compares these three therapies by listing out their principles, applications and symptoms treated.
|
Ultrasound Therapy |
Interferential Current Therapy (IFC) |
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) |
|
|
Principles |
Ultrasound therapy is a mechanical vibration. When sound waves pass through the body tissues, vibration is induced, and part of the kinetic energy is converted to heat energy. |
It utilises two medium frequency currents to pass through the tissues simultaneously to treat the areas. |
Shock waves are audible high-energy sound waves that go through your skin and the affected muscle area. In the medical world, shock waves have been used to disintegrate kidney stones. It uses extracorporeal shockwaves to penetrate the skin and reach the injured part of the tendon. Through generating vapourised blasting and destroying the adhesion of the injured tendons, scars, and even calcified or fibrotic soft tissues. |
|
Applications |
|
|
|
|
Symptoms Treated |
Ultrasound therapy is mainly used to treat soft tissue injury such as:
|
By stimulating peripheral nerves, it can deal with:
|
Shockwave therapy can relieve the following pains:
|
How Ultrasound Therapy, Interferential Current Therapy and Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Are Performed
Different equipment are employed when conducting ultrasound therapy, extracorporeal shock wave therapy and interferential current therapy. The treatments are painless or with slight pain generally.
|
Ultrasound Therapy |
Interferential Current Therapy (IFC) |
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT) |
|
|
Procedure |
A gel is applied to the skin. During the treatment, your therapist would continually move the transducer head over the injured area to deliver the sound waves. |
A suction cup or electrode sticker is stuck on your body. |
Your therapist would use different therapy heads to adjust the wave strength for treating the injury according to your conditions. |
|
Senses during the Therapy |
Painless in general |
Numbness and a sense of ‘electric shock;’ Muscles spasm spontaneously. |
Mild pain and soreness. Bruise or redness on skin which fades in several days. |
|
Intensity |
Mild |
Moderate |
Strong |
|
Treatment Time |
Approx. 10-20 mins |
Approx. 10-30 mins |
Approx. 5-8 mins |
Side effects of Ultrasound Therapy, Interferential Current Therapy and Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy
In general, these therapies do not have severe or long-term side effects if the treatments are conducted by a professional therapist. When receiving ESWT, there may be mild pain, soreness, bruise or redness temporarily that disappear within a few days.
Conditions Where Ultrasound Therapy, Interferential Current Therapy and Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Should Not Be Used
The therapies should not be used if:
- The injured area is in acute inflammation.
- There are bacterial infections, tumours or wounds around the pain side.
- You are pregnant.
- You are using an artificial pacemaker.
- You have bleeding disorders.
Costs of Ultrasound Therapy, Interferential Current Therapy and Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in Hong Kong
Ultrasound therapy, extracorporeal shock wave therapy and interferential current therapy are usually considered as an integral part of physiotherapy based on your strain. The local hospital charges for each physiotherapy session is around HK$150, while charges of private clinics are around HK$600 to 1,500 per session. However, some group insurance and medical insurance also cover the costs of physiotherapy.
How Many Treatments Are Necessary?
Based on your conditions, your therapist would suggest performing the treatment twice or thrice a week at first, followed by an evaluation after three to six weeks.
Treat yourself better by healing your chronic muscle and tendon strain! Cigna DIY Health Plan enables you to freely choose from various protection benefits to customise your plan to your individual needs, including dental coverage, regular oral check-up, treatment cost and emergency. Tailor your health coverage now.