Everybody is looking forward to their tan lines or in other words getting a nice bronze skin colour in summer. However, the more sunbathing you have, the greater risk of skin cancer you pose on yourself, as the cancer is closely related to ultraviolet rays and melanin.
Skin cancer is one of the top ten cancers in Hong Kong. In 2018, there were 1,186 new skin cancer cases, which accounted for 3.5% of all new cancer cases in the city. With an uprising trend observed in the number of cases, all outdoor enthusiasts should be aware of this lethal disease and take necessary measures.
What is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer refers to malignant tumours growing on the outermost skin layer (epidermis), which is made up of different skin cells. If these cells grow abnormally and lead to mutation, they will develop into cancer.
There are three types of skin cancer, namely basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and malignant melanoma. The former two belong to non-melanomas and are more common, while the latter is relatively rare and poses a greater threat to one’s health.
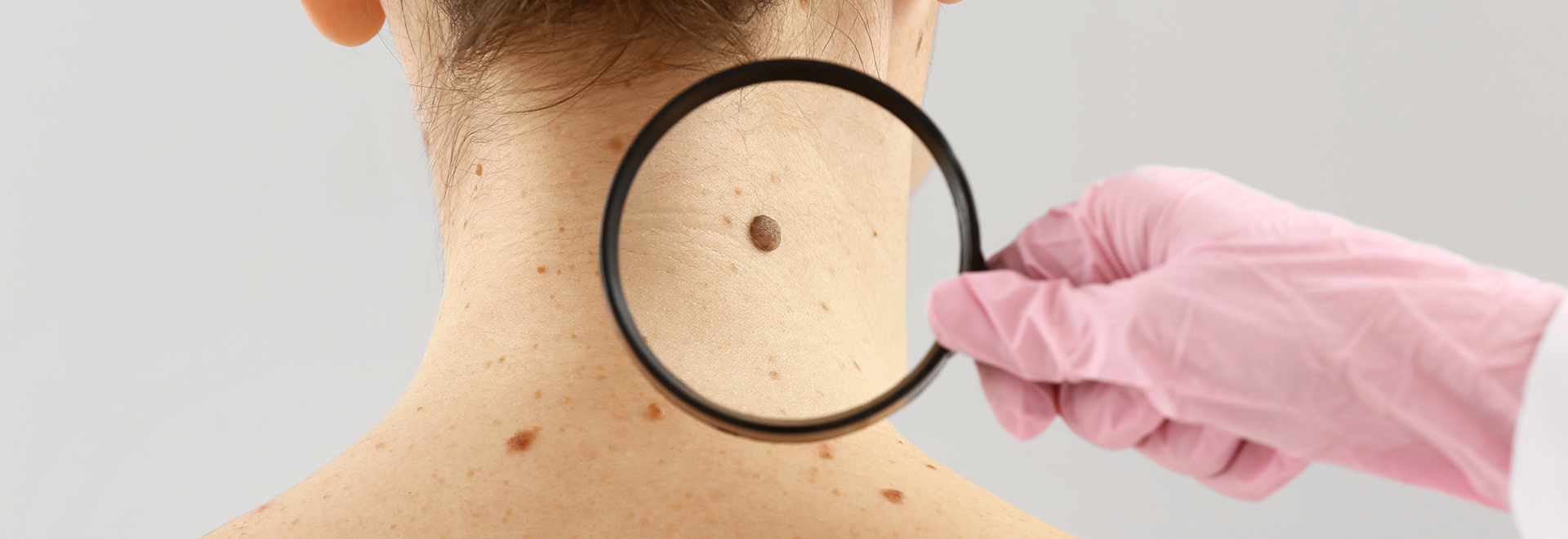
Skin cancer is more likely to develop on the face, neck and arms where the skin exposures to the sun are more frequent.
High-Risk Groups of Skin Cancer
- Prolonged exposure to sunlight (such as athletes, sailors etc.)
- Having had one or more blistering sunburns as a child or teenager increases your risk of developing skin cancer as an adult
- A lighter natural skin colour
- Prone to sunburn but not getting dark
- People who have many moles or abnormal moles called dysplastic nevi are at increased risk of skin cancer
- A family history of skin cancer
- Those who received radiation treatment for skin conditions such as eczema and acne may have an increased risk of skin cancer
- A weakened immune system
Symptoms of Skin Cancer
Each type of skin cancer has its respective appearance and symptoms. Discover skin cancer early by observing signs on your skin and changes in your moles.
|
Types of Skin Cancer |
Appearance and Symptoms |
|
Basal cell carcinoma |
|
|
Squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
Malignant melanoma |
|
How to Perform Self-Examination For Skin Cancer?
By following the ‘ABCDE’ principles, you could distinguish between benign and malignant melanoma.
- A (Asymmetry): One half of the spot is unlike the other half.
- B (Border): The spot has an irregular, scalloped, or poorly defined border.
- C (Color): The spot has varying colours from one area to the next, such as shades of tan, brown or black, or areas of white, red, or blue.
- D (Diameter): While melanomas are usually greater than 6 millimetres, or about the size of a pencil eraser when diagnosed, they can be smaller.
- E (Elevation): The spot looks different from the rest or changes in size, shape, or colour.
Stages and Survival Rate of Skin Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma can be divided into two phases, namely the local phase and metastatic phase.
For malignant melanoma, the staging is from 0 to 4, depending on the extent of the spread and tumour thickness. Stage 4 indicates advanced cancer that has spread to other areas of the body.
The survival rate is high if you receive the treatment at an early stage. In general, the recovery rate of early-stage skin cancer patients can be as high as 90%. If metastasis is observed, the rate is about 27%. However, only 4% of melanoma cases are reported with such deterioration.
Skin Cancer Treatments
There are numerous methods to treat basal cell carcinoma. Apart from surgical removal, laser surgery and electrodesiccation, early skin cancers can be killed by freezing them with liquid nitrogen. The dead tissue sloughs off when it thaws.
Surgical resection is more common for treating squamous cell carcinoma.
For malignant melanoma, surgical excision is used to eliminate the cancer cells. Sometimes, it requires the removal of the dermis for complete deterration of the tumour. In the advanced stage, combined therapy with radiotherapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy or removal of lymphatic tissues is needed in the course of treatments, depending on the extent of skin cancer.
Skin Cancer Prevention Tips
Research shows that 80% of skin cancer cases can be prevented by sun-protective measures. You could follow the tips below to lower your risk of skin cancer.
- Apply sunscreen and cover up with light-coloured clothing, including a broad-brimmed hat and UV-blocking sunglasses.
- Wear sun-protective hats if working outdoors and reduce working hours under the scorching sun.
- See a dermatologist if abnormal changes are observed over moles and birthmarks.
- Keep newborns out of the sun. Use sunscreen on babies over the age of six months.
- Avoid tanning and using UV tanning beds.
Cigna HealthFirst Elite 360 Medical Plan offers comprehensive and personalized medical coverage across the stage prevention, diagnosis, treatment and recovery, with a range of hospital and surgical benefits, optional insurance benefits with an annual limit of up to HK$50 million, personalized health assessment, three critical illnesses(cancer, stroke and heart attack) all-rounded care and international medical concierge service. A 360-degree total health protection that spans across all the key stages of your health journey. Learn more here.
Moreover, Cigna’s first-in-market 'Cancer and Chronic Diseases Care Program at Home' allows you to receive cancer treatments in the comfort of your home, subject to doctor’s recommendations. The Program greatly reduces the risk of infection to you and your family members and ensures an entire focus on your treatment and well-being.