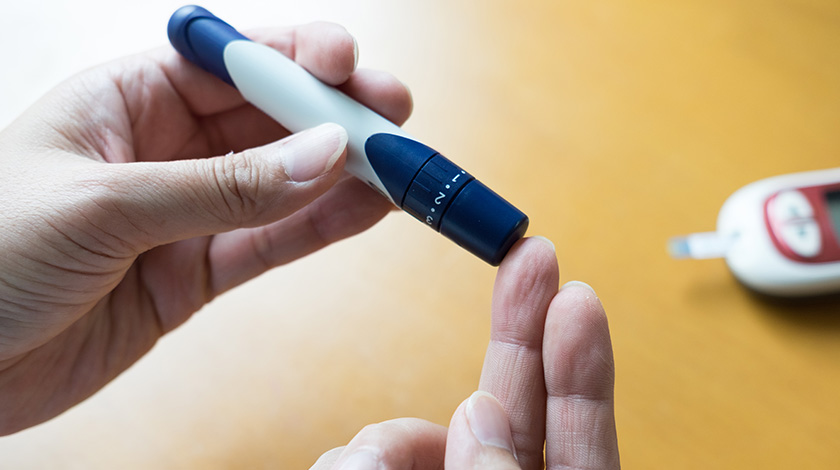
Know Your Enemy — Fighting Diabetes
In 2017 alone,diabetes led to almost 14,000 hospital in-patient discharges and deaths in Hong Kong.And as our diet get increasingly unhealthy and with smartphones, televisions and laptops conspire to keep us away from the treadmill and weights room, those numbers are set to increase. The good news? Diabetes is preventable, and it is always best to know our enemy before fighting it.
Understanding Diabetes
The pancreas is the organ responsible for producing insulin, a hormone that helps the body use glucose (blood sugar) from the food you consume to fuel bodily functions.
For a healthy person, insulin acts like a key that “unlocks” the door between your bloodstream and the cells of your muscles and tissues, so that glucose can pass through and be processed for energy. For diabetes sufferers, the pancreas either does not make enough insulin or the body is unable to make full use of the insulin the pancreas produces, sending your blood glucose levels sky-high.1
What causes diabetes?
The evidence emerging from the millions of dollars invested in diabetes research clearly points to two categories of high-risk factors.2
- Genetic factors: The first is heredity. For example, statistics suggest that Caucasians over the age of 40 are at a higher risk of developing diabetes. In addition, a family history of diabetes is a strong predictor of diabetes in later life. These, unfortunately, are factors we have no control over.
- Lifestyle factors: The second consists of lifestyle factors — mainly diet and exercise. Diets that are high in calories, sugar and saturated fat, combined with a sedentary lifestyle, put you at a severe risk of developing diabetes.
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes is often called juvenile or early onset diabetes because it is much more common in children (usually manifesting before the age of 15) than adults. This type of diabetes occurs when the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Managing this condition therefore involves regular blood sugar monitoring and insulin injections.2
Type 2 Diabetes:
Type 2 diabetes accounts for a stunning 85% of diabetes incidences and is most commonly diagnosed in people over the age of 40. Type 2 diabetes is managed by regular exercise, diet management and careful blood sugar monitoring that is often supplemented by oral medication and insulin injections.2
Pre-diabetes:
If your blood sugar is higher than normal, but still not high enough to be classified as Type 2 diabetes, you fall into the pre-diabetes category. The good news is that you still have the opportunity to take action. Fending off this impending illness will require great commitment, including vigorous physical exercise for as many as five 30-minute sessions a week and a strict diet with very few simple carbohydrates and sugars.2
Ways To Help Control Diabetes
There are no obvious symptoms for some diabetics. However, without proper control, a continuously high blood sugar level may lead to various chronic complications including coronary heart disease, blindness, chronic renal failure, stroke or even death in severe cases. Learn to live with diabetes by controlling blood sugar levels to reduce the risk of complications.
- Stay positive: It is common for diabetics to feel stressed and worried, but negative emotions such as anxiety will make the body release adrenaline which can raise blood sugar. Staying positive is also a good way to motivate one to control blood sugar for better health.
- Low-Carb diet: High intake of carbohydrates is a major factor in raising blood sugar. Three main types of food containing carbohydrates are grains, dairy products and fruits. Diabetics can lower their intake of rice by half to reduce carbohydrates absorption. With high-fibre vegetables and low-fat meats, a balanced diet can help stabilize blood sugar level.
- Exercise regularly:Regular exercise can help reduce weight and prevent insulin resistance. It is recommended to carry out 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity every week. Or you can just begin to walk more. Live a more active life can help you control blood sugar level.
- Take medicines: Follow your doctor’s instructions and take your medicines for diabetes even when you feel good. Taking oral hypoglycemic drugs or insulin injections are all effective ways to control blood sugar. Receive appropriate treatments to help reach your blood sugar target effectively.
- Blood Glucose Monitoring:You can better understand the changes in blood sugar level with blood glucose monitoring. This is essential in helping you adjust your diet and activity level to achieve better control of blood sugar.
How To Prevent Diabetes
If you’re lucky enough to have a healthy body, then treasure it. Live your life by the old maxim, “my body's a temple”. Have a healthy diet full of complex carbohydrates like brown rice and whole wheat bread and keep indulgences in fatty or sugary foods to a minimum.
Stay active by participating in sports, workout classes or even just taking regular walks. These modest lifestyle changes can keep diabetes away.
Cigna HealthFirst Elite 360 Medical Plan offers comprehensive and personalized medical coverage across the stage prevention, diagnosis, treatment and recovery, with a range of hospital and surgical benefits, optional insurance benefits with an annual limit of up to HK$50 million, personalized health assessment, three critical illnesses(cancer, stroke and heart attack) all-rounded care and international medical concierge service. A 360-degree total health protection that spans across all the key stages of your health journey. Learn more here.
Sources:
- What is diabetes? Diabetes UK. Visited 28 March 2014.
- Diabetes risk factors. Diabetes.co.uk. Visited 28 March 2014.
- http://www.chp.gov.hk/en/content/9/25/59.html. Visited 13 May 2017.
- 香港糖尿聯會 - 與糖尿病共處
- 智抗糖 - 糖尿病如何降血糖?控制血糖五原則